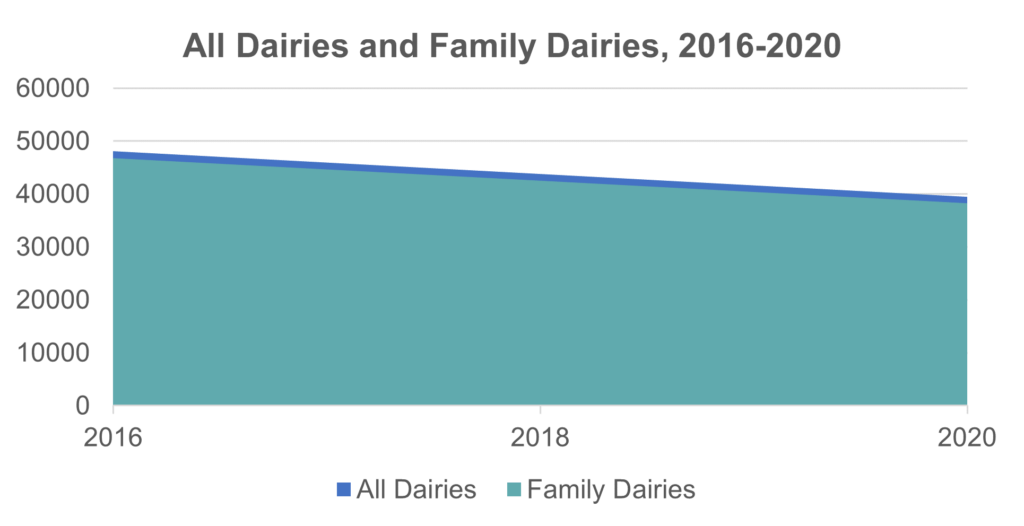
The “decline of the family farm,” purportedly replaced by the “rise of the corporate farm,” for generations has been one of the most well-trodden – and inaccurate – tropes in conversations about U.S. agriculture. It’s true, the number of dairy farms has declined. But that consolidation hasn’t diminished the dominance of family-run dairies. It’s meant that smaller family farms have generally become a bit larger, often to support additional family members coming into an existing operation.
Of an estimated 39,442 farms of all sizes with dairy cows in 2020 – a comprehensive number that’s higher than the number of licensed dairy operations — 38,286 of them were family-operated, according to USDA data. That’s 97.1 percent of dairies, an extremely high percentage that isn’t budging with consolidation. In 2016, for example, even though the overall number of farms with dairy cows was more than 48,000, the family-farm percentage that year was 97.3 percent – a remarkably consistent figure.
What’s going on? The same thing that’s been going on for generations. Dairy farmers sell their cows to fund their retirements. Farmers whose children don’t want to take over the farm sell to the farmer whose children will. A small number of “corporate farms” do exist, and because they tend to be larger, they produce a disproportionate (but still small) percentage of milk. But when dairy farms consolidate, as a rule, they consolidate into other family farms. And the fewer, larger farms that remain are still decidedly family operations.
Just as dairy itself isn’t dead, the family dairy farm isn’t either. But like everything else, it’s changed. A family dairy farm may be a bigger employer than before, and it may be a more sophisticated business. That’s been the direction of U.S. agriculture for generations, and that’s true whether a farm has 80 cows, or thousands. Just look at the average size of a U.S. dairy farm. It’s grown from about 50 cows in 1990 to about 300 cows today. Despite the realities of an ever-changing industry, the family farm remains the bedrock of U.S. dairy farming. And that shows no sign of ending, anytime soon.