
Source: Michigan State University
Zachariah Rutledge, Michigan State University Department of Agricultural, Food, and Resource Economics; and Phil Durst, Michigan State University Extension
While labor-saving technology has increased productivity, people are still an integral part of cow care. In this article we’ll provide context and highlight strategies to help address labor challenges.

Oh, the labor pains! How often we hear from farm owners that they can’t find enough people willing to work on the farm. Dairy production is labor-intensive, with cows being milked, fed, moved and managed around the clock. Compounding these challenges, the labor market is increasingly tight for a number of reasons, including a declining interest in farming among younger generations, a declining pool of workers who are willing to do farm work, and few legal channels for immigrant labor. While labor-saving technology has increased productivity, people are still an integral part of cow care. In this article we’ll provide context and highlight strategies to help address labor challenges.
Background
Most hired farm employees in the United States were born in Mexico. Mexico’s close proximity to the US, and its relatively poor economic conditions, incentivized migration to the US during the 1900s and early 2000s. Many of these migrants entered the US without legal authorization and sought work on US farms. High levels of Mexico-US migration enabled US agricultural producers to maintain access to an abundant supply of relatively inexpensive labor and expand production to satisfy increased demand.
However, in recent years, US farm labor markets have undergone substantive structural changes that have increased the prevalence of labor shortages. Labor supply pressures drive farm wages up, stunt growth opportunities for American farmers, accelerate the adoption of labor-saving technologies, and force production to other countries that have lower production costs. These trends raise concerns about the economic viability of dairy farming in Michigan and the production capacity of Michigan’s dairy industry.

Dairy labor costs are rising and employment is declining
The year 2015 marked an inflection point in Michigan’s dairy labor market, when the growth of real labor costs (i.e., adjusted for inflation into 2022 dollar values) started rising and employment growth started tapering off. Figure 1 shows that between 2000 and 2015, the real average hourly wage (in $2022) of animal-related farm employees in the Lake Region was relatively stable in the $13.00 to $14.00 range. In 2017, the average real wage (in $2022) reached an all-time high of $15.65 and has continued to rise. In 2022, the average real wage was $16.90.
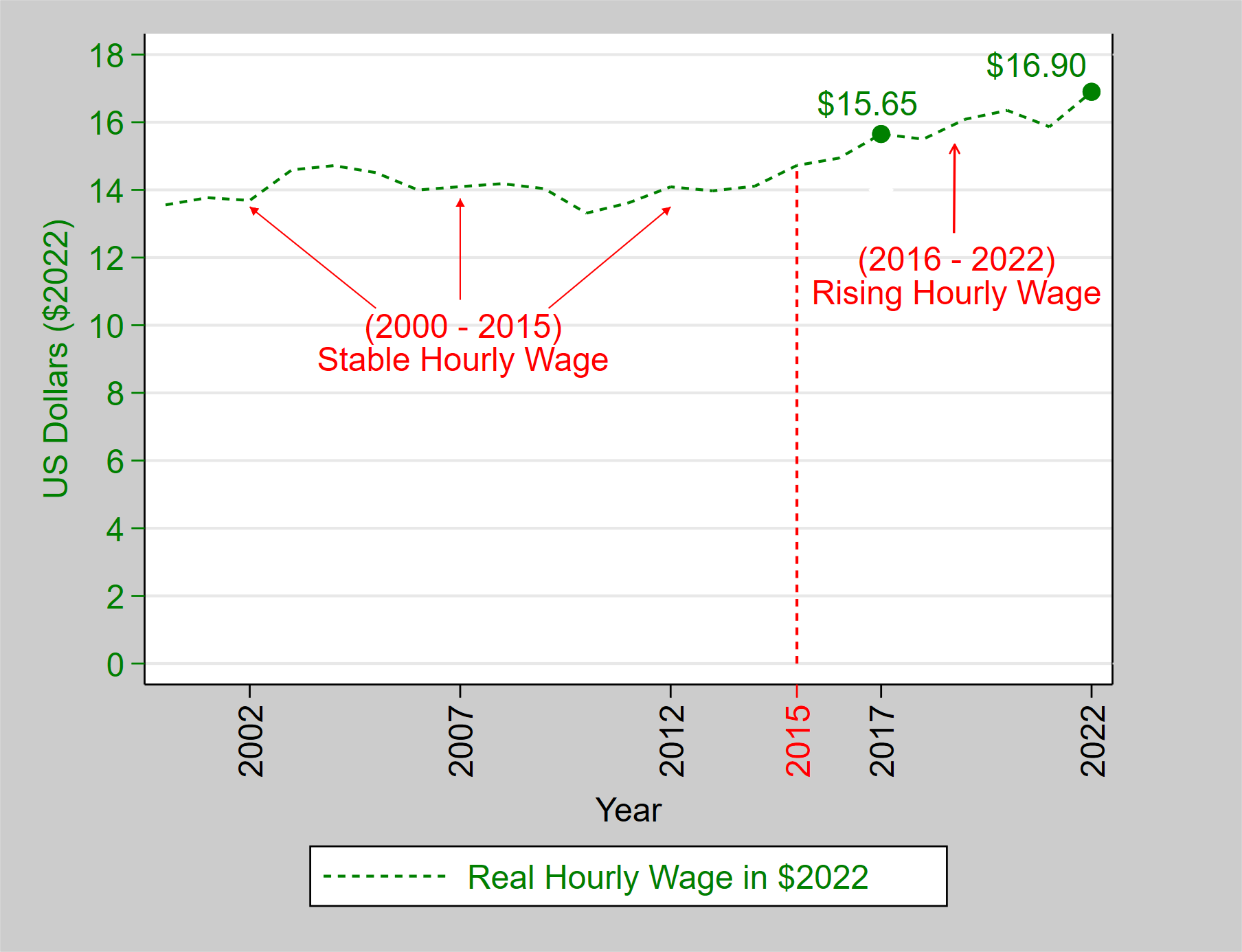
Dairy employment has dropped every year since the 2017 peak, and there were 500 fewer year-round-equivalent jobs on the books of Michigan dairy farmers in 2022 relative to 2017 (Figure 2). Economic theory suggests that when a labor market is experiencing a decline in the supply of labor, wages will rise, and employment will drop. These recent trends are consistent with a declining supply of dairy farm labor in Michigan.
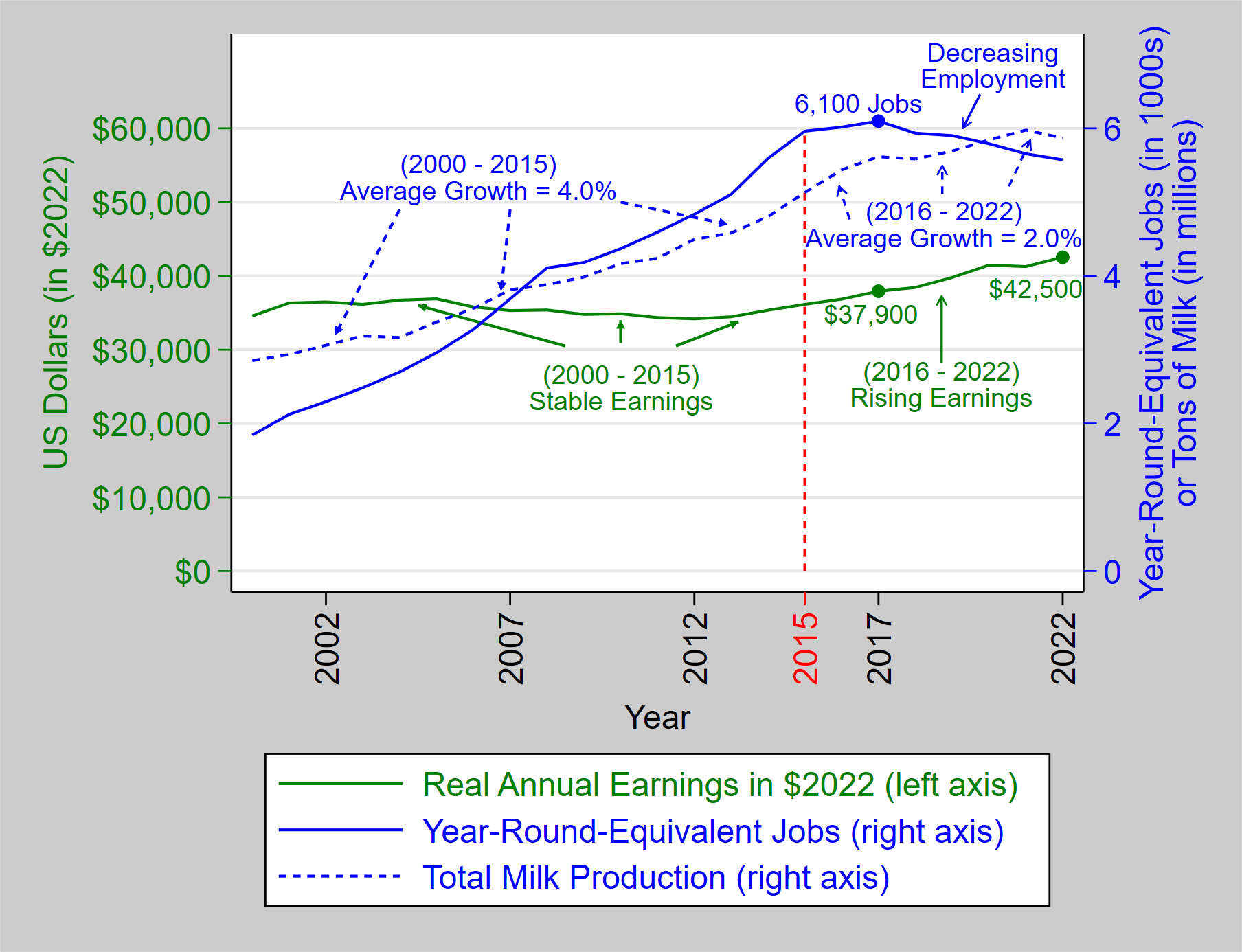
Since 2015, the growth in total milk production declined to an average 2 percent per year. While there are many factors that can slow milk production growth (including increased building costs and processing capacity limits), a decrease in labor availability, as indicated by the reduction in farm employees, may also be a factor limiting growth.
Value for investment
Rising income for dairy employees is not the problem, as long as productivity increases faster than wages. Therefore, it is important to look at efficiency and consistency in work. Unfortunately, many farms report problems with their employees, including failure to show up for work, a lack of concern about the success of the farm, and employee turnover. These problems decrease efficiency and consistency and exacerbate the farm labor availability problem. Figure 2 shows that dairy production growth started declining in the wake of rising labor costs and reduced employee availability. In fact, in 2018 and 2022, Michigan experienced declines in milk production relative to the previous year.
Employee disengagement and turnover are costly, not only in terms of wages wasted, but also in terms of employee morale, quality of work and product, and safety for all. Many farmers recognize the importance of developing positive relationships with the people who work for them. Open and honest communication regarding expectations, farm goals, how the employee’s work contributes to those goals, and employee performance are key factors that can help employees develop a personal commitment to the success of the farm.
A study published by Moore et. al. (2019) concluded that “the importance of an employee’s relationship with their supervisor and other employees cannot be overstated. The relationship can have a positive or negative effect on (employee) satisfaction, longevity and recruitment.” Employees serve a critical role in job recruitment efforts because they are often the ones that refer other workers to the farm. Satisfied employees are more likely to recommend the farm as a place to work to individuals who share their commitment to work. As such, when farm owners and managers develop good relationships with their employees, they will improve the quality of the work environment and expand the pool of quality employees seeking to work on their farm. In a tight labor market, this factor can make the difference between a farm that is able to grow and one that cannot because it cannot attract or retain a high-quality workforce that is committed to the farm.
While the availability of immigrant farm employees is declining, foreign-born workers will continue to serve a critical role in the farm workforce. If farmers want to expand the pool of employees that are able and willing to work on their farms, they may want to consider participating in agricultural labor policy reform discussions that are being held at the local, regional, and national levels. Moreover, developing business management strategies that improve the work environment and help employees feel connected to the business can help retain and expand the pool of high-quality employees.
Employee leadership tips
- Consistently build team mentality; teach and model an attitude of helping one another and being responsible to others.
- Communicate regularly about business performance; provide individual feedback soon for both good and lacking performance.
- Respect employees as people; listen to them and ask them to respect your decisions. Teach them why you set your methods and standards the way you do.
- Provide regular opportunity for employee development; teach cattle evaluation practices, have visiting consultants talk with employees, and don’t underestimate their desire to learn.
- Involve employees in making decisions; whether hiring or purchasing decisions, employees can provide valuable input that makes them vested in the results.
Conclusion
Labor is a critical component of any farming operation. Labor supply constraints can reduce the economic viability of farming and reduce production capacity. In some cases, automation may replace labor inputs and reduce labor costs, but these types of investments can be expensive. For many farming operations, investing in costly technology solutions is not economically feasible, and having access to employees who are qualified and willing to perform farm work is the only viable option. Based on the current trajectory of employment and production in Michigan’s dairy sector, the dairy industry in the state may be constrained by labor availability. If employment continues to decline and solutions are not found, milk production capacity could decline within the next few years. Farmers can take steps in their own businesses to foster positive relationships with their employees and enhance the work environment, which can help improve efficiency and reduce employee turnover.
Michigan State University is committed to understanding the labor challenges our state is facing, exploring potential solutions to the problem, and helping farmers improve their employee leadership skills.








